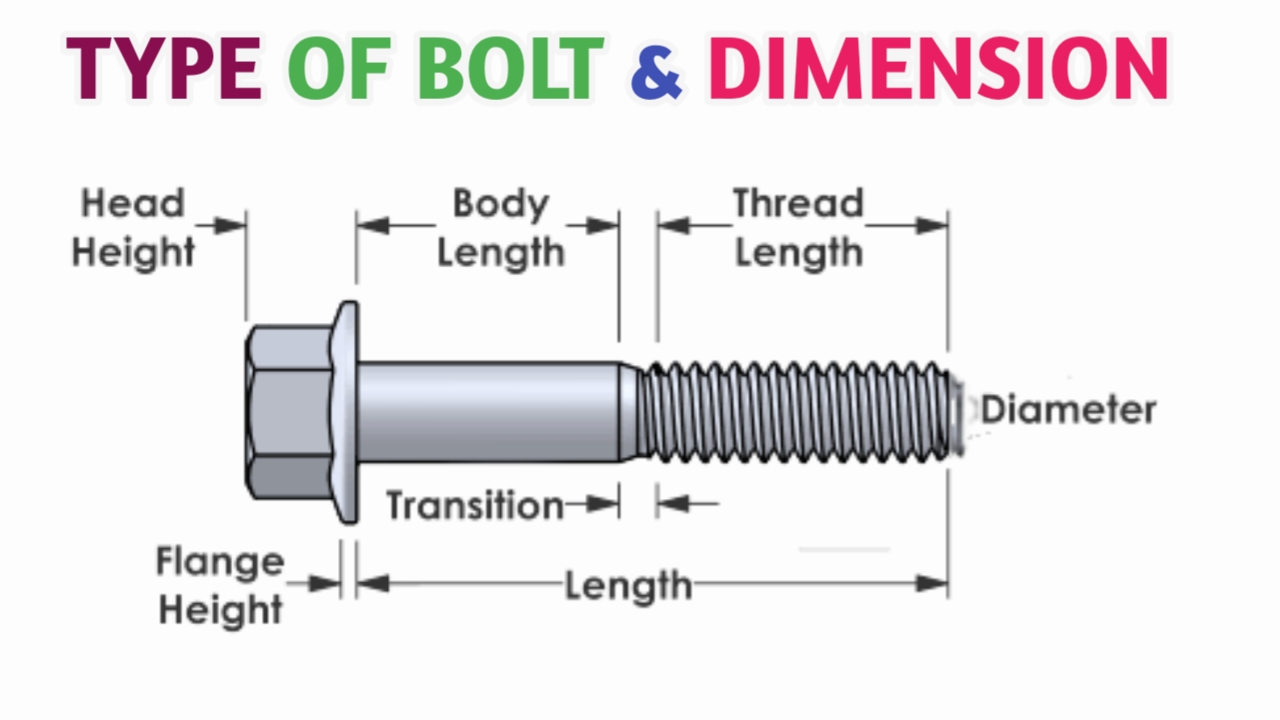
Types of bolts encompass a wide variety of fasteners used in construction, engineering, and manufacturing. Bolts are crucial components for joining materials together securely. Here’s a breakdown of common types:
There are various types of bolts, each designed for specific purposes. Let’s explore some of them
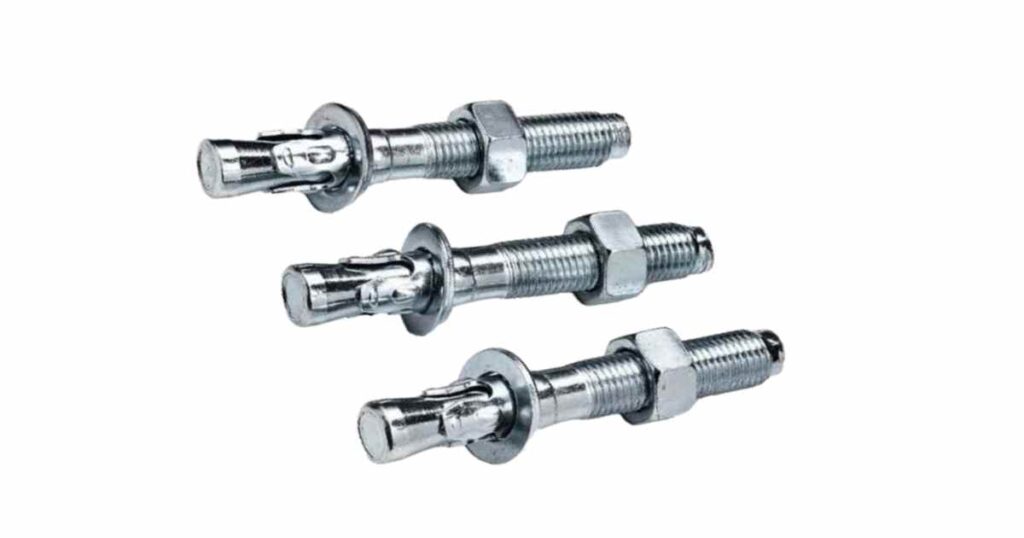
1. Anker Bolts:
These bolts are used to connect concrete to structural and non-structural components Steel columns are often used to fix reinforced concrete foundations or facades systems to concrete walls, where they transfer tensile and shear forces

2. Arbor bolt:
Arbor bolts, specifically designed for miter saws, secure the tool and hold the blade in place They are already assembled and have a washer permanently attached to the tip Arbor bolts are designed with a sunken head and often have reverse threads

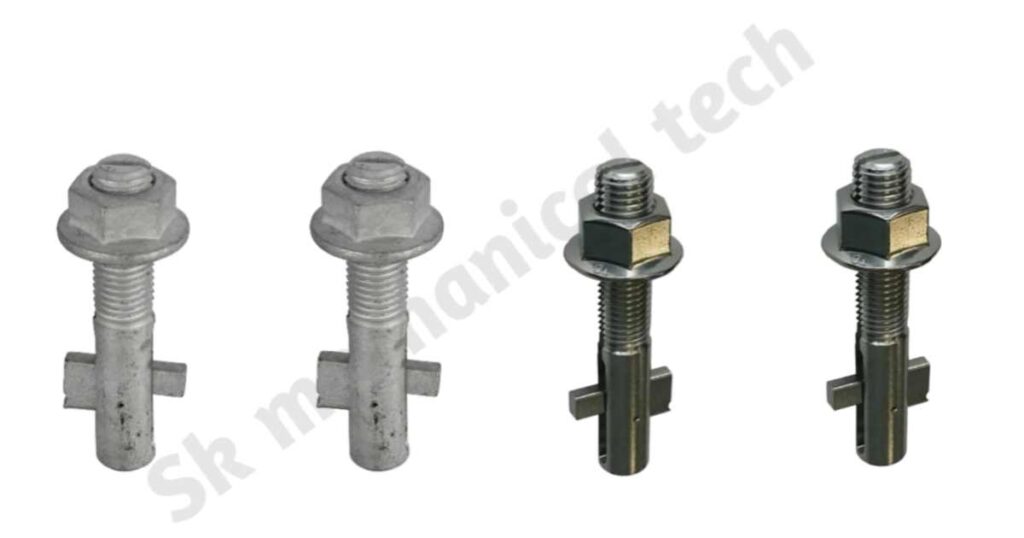
3. Blind bolts:
Compared to conventional rivets or welds, these structural fasteners offer greater conformability and strength. When rivets or hex bolts are difficult to use, blind bolts are the best option.

4. Carriage Bolt:
Coach bolts have a round head and a square neck. They are often used to connect wood to metal, like binding wooden beams to metal plates
read more-
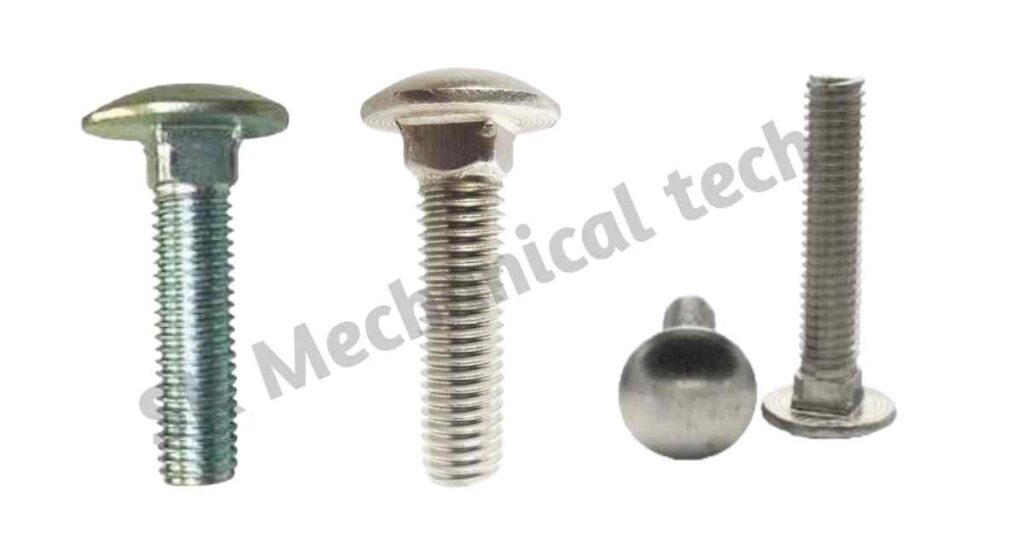

6. Elevator Bolts:
Flat, smooth, and countersunk heads are elevator bolts. Conveyor systems, grain elevators, and other places where a flush surface is needed are places where they are most commonly used
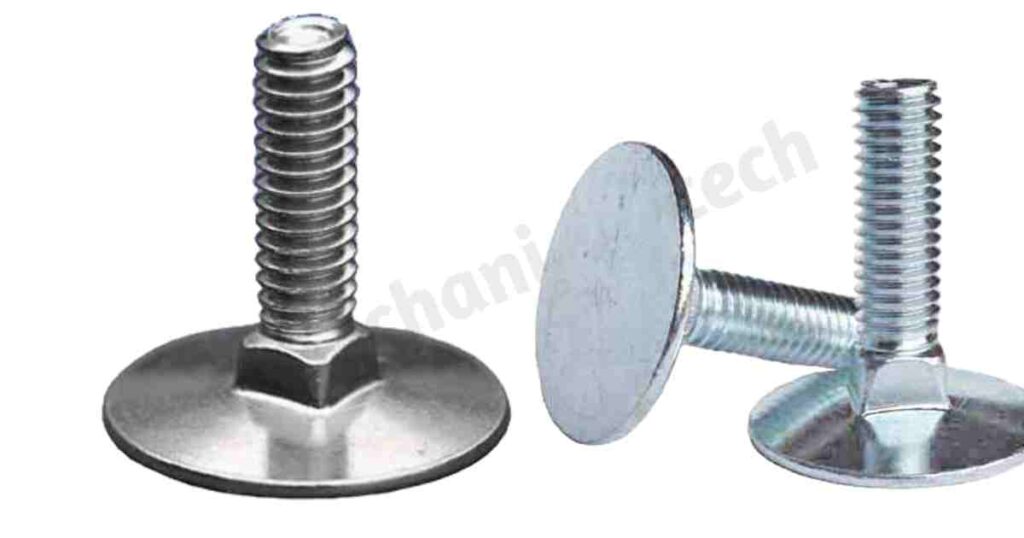

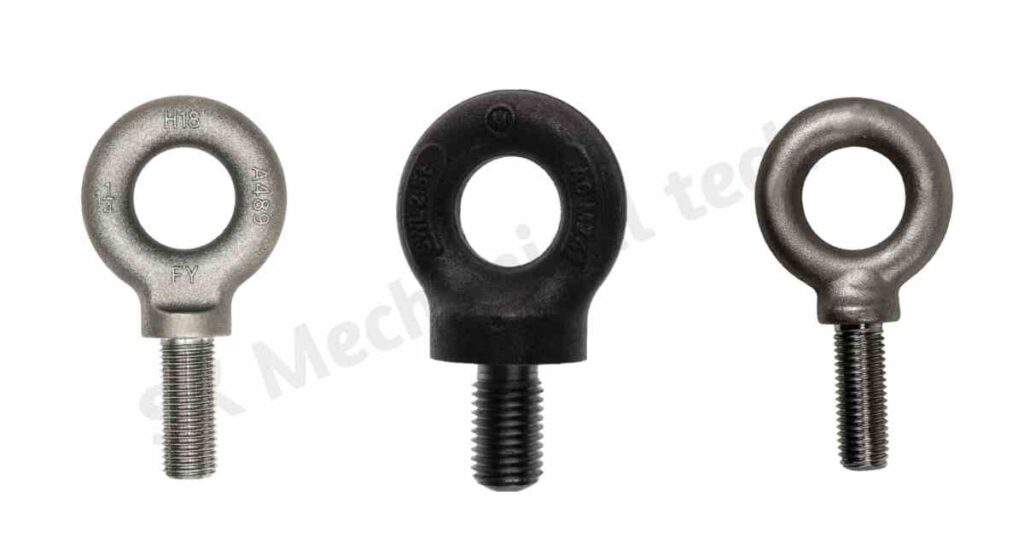
Eye Bolts: These bolts have a looped head, or eye, and they are used to lift or secure things. Most of the time, they are placed on concrete or wood surfaces

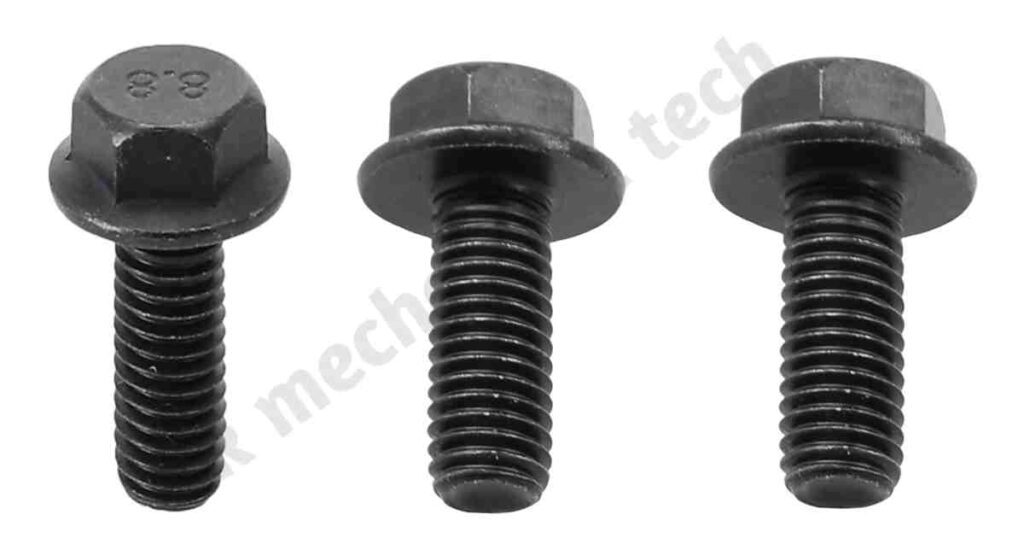
7, Flange Bolts:
Under the head of a flange bolt, there is a wide, flat flange that distributes loads and prevents them from turning. They are frequently used in automobiles and machinery.

8. Hex Bolt:
Hexagonal head hex bolts, also called hex cap screws, are threaded along their entire length. They are widely used in the construction, machinery, and automotive industries because they are versatile.

Each bolt type has a specific function, so choosing the right one depends on the use and load requirements.
What is the difference between a bolt and a screw?
Let’s explore the key differences between bolts and screws:
- Thread Type:
- Bolts: Bolts have a screw thread, or external thread, along their entire length. They are inserted through holes, and on the opposite side, they are secured with nuts.
- Screws: Screws, which have an internal thread, also known as a helix groove, are designed to be driven directly into a material like wood or metal without having to use a separate nut.
2. Purpose:
- Bolts: Bolts are used to connect two or more parts. They create a strong and long-term connection.
- Screws: Screws are used to fix materials together or fix things to surfaces. They can also be used for clamping parts or holding them in place.
3.Application:
- Bolts : Mainly used in structural applications, machinery, construction, and car assemblies
- Screws : are widely used in woodworking, assembling furniture, electronics, and general housework
4.Head Shape:
- Bolts: Normally, bolts have a hexagon (hex bolt) or a specialized head shape (car bolt).
- Screws: count, flat, round, and pan head screws are available.
5. Nut Requirements:
- Bolts: Different notes are needed to set them up.
- Screws: It does not require a distinct nut; they self-tap and make their own threads.
6. Materials:
- Bolts :: often made of strong steel or other durable materials.
- Screws : Available materials include steel, brass, aluminum, plastic, etc.
Remember that while screws and bolts both perform essential functions, understanding their differences helps in choosing the best fastener for certain purposes.