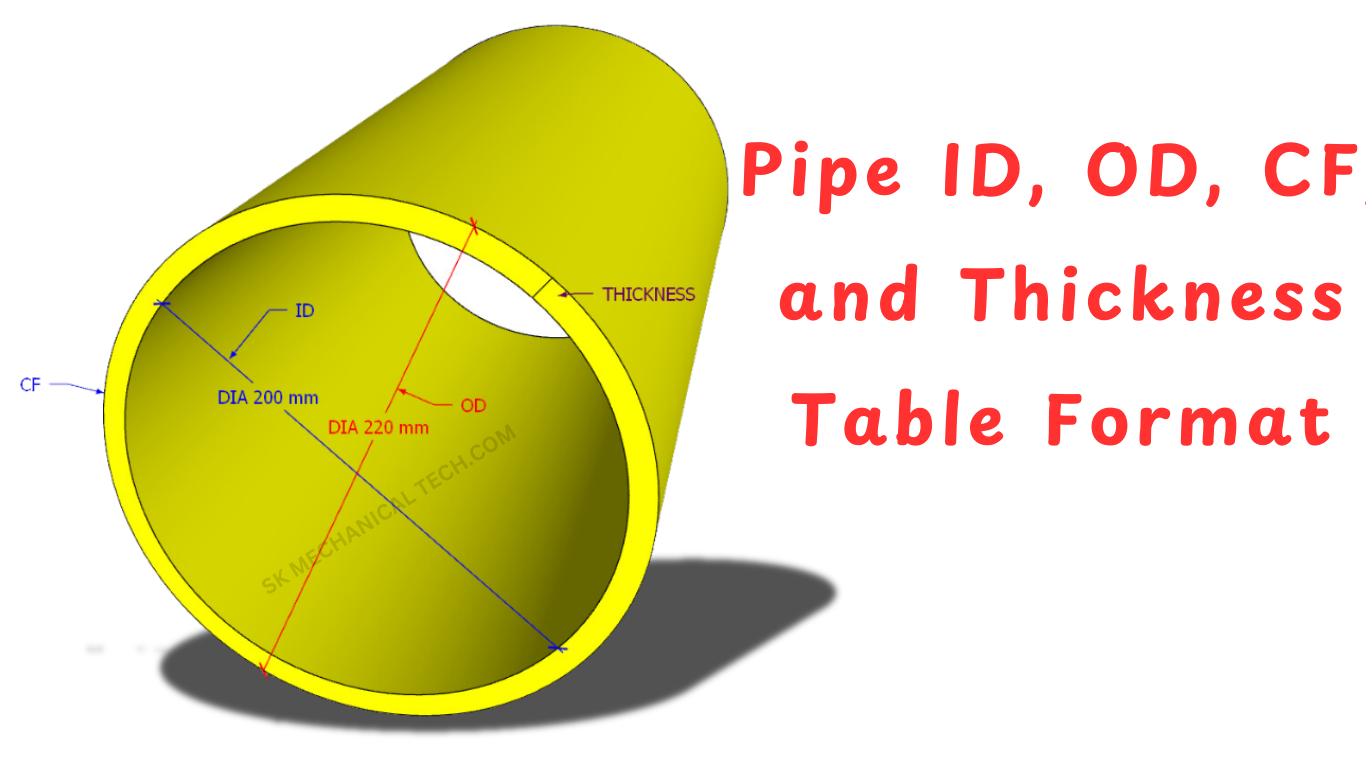
Introduction
Pipes are an essential part of various industries, including construction, plumbing, oil and gas, and manufacturing. Understanding pipe dimensions such as Inside Diameter (ID), Outside Diameter (OD), Circumference (CF), and Thickness is crucial for selecting the right pipe for specific applications. This article provides a comprehensive guide and table format to help users easily find these critical parameters.
Understanding Pipe Dimensions
1. Outside Diameter (OD)
The Outside Diameter (OD) is the total diameter of the pipe, measured from one outer edge to the other. It is a fixed dimension for a given nominal pipe size (NPS).
2. Inside Diameter (ID)
The Inside Diameter (ID) is the actual internal diameter of the pipe. It varies based on the wall thickness and is crucial for calculating flow rates and pressure ratings.
3. Wall Thickness (T)
The wall thickness of a pipe determines its strength and pressure-bearing capacity. It is generally specified in schedules such as SCH 10, SCH 40, SCH 80, etc.
4. Circumference (CF)
The Circumference (CF) is calculated using the formula:
This factor is used in various engineering calculations for fluid flow and pressure loss.
Pipe Dimension Table Format
Below is a standard table format that provides a structured overview of pipe dimensions:
| Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) | Outside Diameter (OD) | Wall Thickness (T) | Inside Diameter (ID) | Circumference (CF) (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2″ | 21.3 mm | 2.77 mm | 15.8 mm | 66.99 mm |
| 3/4″ | 26.7 mm | 2.87 mm | 21.0 mm | 83.96 mm |
| 1″ | 33.4 mm | 3.38 mm | 26.6 mm | 104.96 mm |
| 1-1/2″ | 48.3 mm | 3.68 mm | 40.9 mm | 151.67 mm |
| 2″ | 60.3 mm | 3.91 mm | 52.5 mm | 189.43 mm |
| 3″ | 88.9 mm | 5.49 mm | 77.9 mm | 279.36 mm |
| 4″ | 114.3 mm | 6.02 mm | 102.3 mm | 359.08 mm |
| 6″ | 168.3 mm | 7.11 mm | 154.1 mm | 528.74 mm |
| 8″ | 219.1 mm | 8.18 mm | 202.7 mm | 688.99 mm |
| 10″ | 273.0 mm | 9.27 mm | 254.5 mm | 857.78 mm |
| 12″ | 323.8 mm | 10.31 mm | 303.1 mm | 1017.81 mm |
| 14″ | 355.6 mm | 11.13 mm | 333.3 mm | 1117.90 mm |
| 16″ | 406.4 mm | 12.70 mm | 381.0 mm | 1277.98 mm |
| 18″ | 457.2 mm | 14.27 mm | 428.7 mm | 1438.05 mm |
| 20″ | 508.0 mm | 15.09 mm | 477.8 mm | 1598.14 mm |
| 24″ | 610.0 mm | 17.48 mm | 575.0 mm | 1915.62 mm |
| 30″ | 762.0 mm | 19.05 mm | 723.9 mm | 2393.20 mm |
| 36″ | 914.0 mm | 22.23 mm | 869.5 mm | 2870.79 mm |
| 42″ | 1067.0 mm | 25.40 mm | 1016.2 mm | 3348.34 mm |
| 48″ | 1219.0 mm | 28.58 mm | 1161.8 mm | 3825.90 mm |
Read more-
- पाइप फिटिंग के प्रकार और उनके उपयोग (25 पाइप फिटिंग नाम और विवरण)
- Elbow Any Degree cutting Formula
- pipe fitter interview questions and answers
Importance of Pipe Dimensional Data
- Engineering and Design: Helps engineers choose the right pipe for structural and fluid flow applications.
- Manufacturing and Fabrication: Ensures precise cutting, welding, and fitting during fabrication.
- Hydraulic Calculations: Essential for pressure loss calculations, flow rate analysis, and system efficiency.
- Standardization: Ensures compatibility across different industrial standards (e.g., ANSI, ASME, API).
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between ID, OD, CF, and wall thickness is essential for selecting the correct pipes for different industrial applications. The table format provided above simplifies the process by presenting all essential dimensions in a structured manner. For specific projects, always refer to industry standards and manufacturer specifications to ensure accuracy.