Introduction | परिचय
Pipe thickness — सुनने में तो ये टॉपिक सीधा-सादा लगता है, लेकिन ये mechanical, civil, और piping engineers के लिए बहुत critical concept है। चाहे oil and gas industry हो या water supply systems, सही pipe thickness चुनना safety और efficiency दोनों के लिए जरूरी है।
इस blog में हम जानेंगे:
Pressure, material, temperature का क्या असर पड़ता है thickness पर
Pipe thickness क्या होता है?
Pipe thickness का formula क्या है?
Example से समझेंगे calculation
Pipe schedules क्या होते हैं?
What is Pipe Thickness? | पाइप थिकनेस क्या होती है?
Pipe thickness simply means दीवार की मोटाई (Wall Thickness) — यानि कि पाइप के अंदर और बाहर की सतह के बीच की दूरी।
इसे हम दो तरह से जानते हैं:
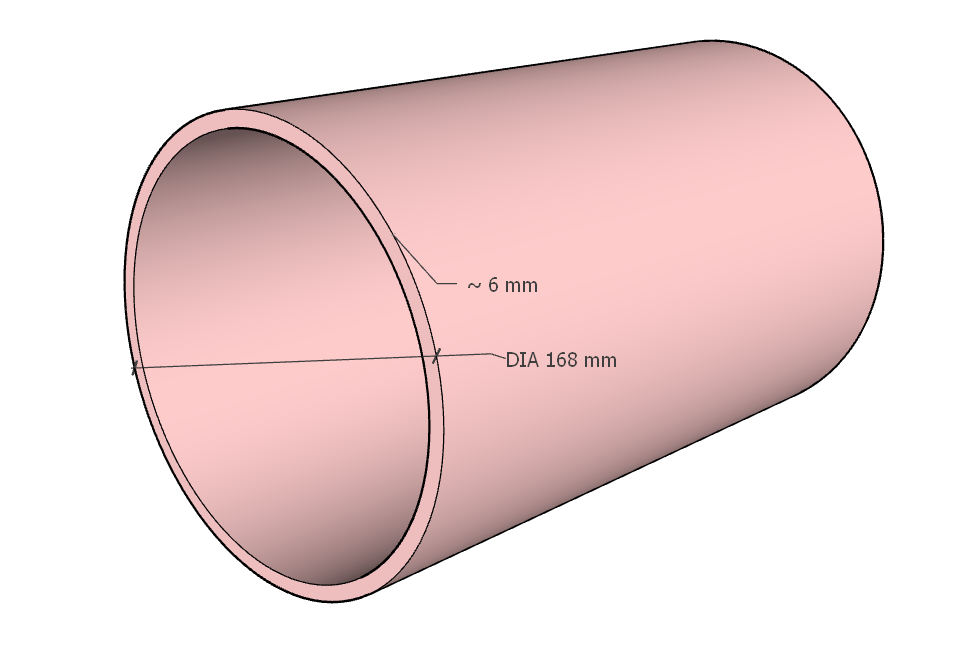
- Nominal Pipe Thickness – जैसे कि SCH 40, SCH 80 etc.
- Actual Thickness (t) – जो calculated या measured thickness होती है।
Wall thickness बहुत important होती है क्योंकि:
- ये पाइप की strength बताती है
- Internal pressure withstand करने की capacity इसी पर depend करती है
- Safety और leak-proof design के लिए critical होती है
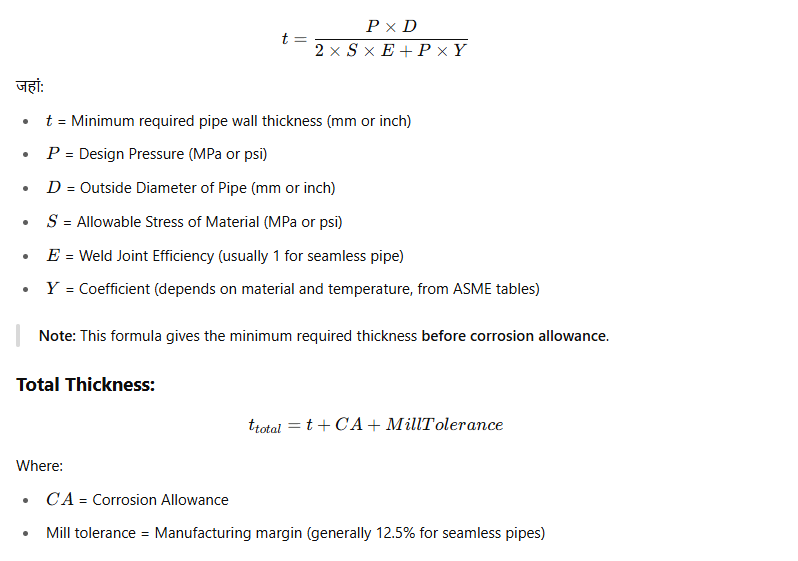
Pipe Thickness Formula (ASME B31.3)
Pipe thickness calculate करने के लिए सबसे commonly used formula है ASME B31.3 code के अनुसार:
Formula:
Example Calculation | उदाहरण के साथ समझें
चलो अब एक example लेते हैं जिससे सारी calculation clear हो जाए।
Given:
- Design Pressure (P) = 5 MPa
- Outside Diameter (D) = 168.3 mm (6-inch pipe)
- Allowable Stress (S) = 137 MPa
- Weld Joint Efficiency (E) = 1 (Seamless Pipe)
- Coefficient (Y) = 0.4 (from ASME table)
- Corrosion Allowance (CA) = 3 mm
- Mill Tolerance = 12.5%
Step-by-Step Calculation:
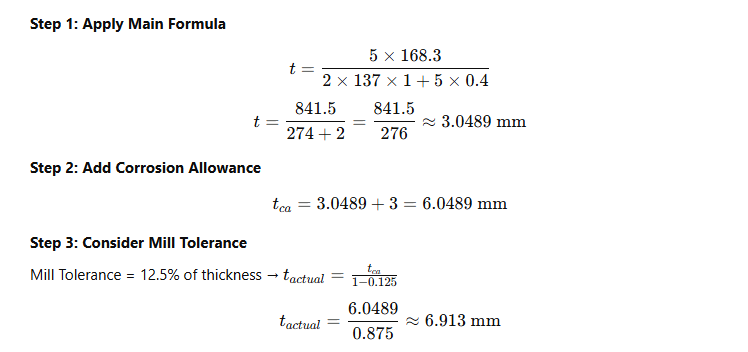
✅ Final Required Thickness = 6.91 mm
इसका मतलब, हमें ऐसा pipe चाहिए जिसकी wall thickness कम से कम 6.91 mm हो — ताकि वो 5 MPa pressure safely handle कर सके।
read more-
- Pipe ID, OD, CF, and Thickness Table Format
- ISA Angle Sizes in India: Comprehensive Details and Guide
- Pipe fitting hacks for beginners: master the basics!
Pipe Schedules और Thickness | SCH क्या है?
Piping industry में pipe thickness को “Schedule” numbers से भी represent किया जाता है — जैसे:
- Schedule 10
- Schedule 40
- Schedule 80
- Schedule 160
- XXS (Double Extra Strong)
Example:
| Pipe Size | SCH 40 Thickness | SCH 80 Thickness |
|---|---|---|
| 6 inch | 7.11 mm | 10.97 mm |
Schedule number बढ़ने पर thickness भी बढ़ती है — जिससे pressure handling capacity भी बढ़ती है।
📌 Note: Actual thickness depends on nominal pipe size (NPS), schedule number से exact thickness ASME B36.10 standard से मिलती है।
5. Material & Temperature का असर
Material Stress Value (S):
हर metal की अलग strength होती है:
| Material | Allowable Stress (MPa) |
|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | ~137 MPa |
| Stainless Steel | ~138-150 MPa |
| Alloy Steel | Higher |
Temperature के साथ Material कमजोर हो सकता है:
जैसे-जैसे temperature बढ़ता है, metal की strength कम होती जाती है — इसलिए high temp applications में ज्यादा thickness चाहिए।
Y Factor
Table (approximate):
| Material | Temp (°C) | Y Value |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | < 427°C | 0.4 |
| Stainless Steel | < 538°C | 0.4 |
| Alloy Steel | > 540°C | 0.7 |
Common Mistakes in Pipe Thickness Calculation
- Ignoring corrosion allowance: Real-life environments always cause corrosion.
- Not considering mill tolerance: Pipes are never manufactured at exactly the theoretical thickness.
- Wrong units: MPa vs psi, mm vs inch — ध्यान रखें।
- Incorrect joint efficiency: For welded pipes, E < 1 हो सकता है।
- Temperature neglect: Material strength temp से degrade होती है।
Thickness Calculation in Excel
बहुत से engineers Excel में ये calculation करते हैं। Here’s a simple formula:
excelCopyEdit= (P*D)/(2*S*E + P*Y)
Cell wise:
- A1: Pressure (P)
- A2: OD (D)
- A3: Stress (S)
- A4: Efficiency (E)
- A5: Y
Formula in A6:
markdownCopyEdit= (A1*A2)/(2*A3*A4 + A1*A5)
Want me to send a sample Excel template? Just ask! 😊
Thickness vs Pressure Rating | Class 150, 300, 600 क्या है?
Flanges और valves में हम pressure class देखते हैं:
| Pressure Class | Approx. Pressure (psi) |
|---|---|
| 150 | ~285 psi |
| 300 | ~740 psi |
| 600 | ~1480 psi |
Higher pressure class → Higher required pipe thickness → Higher cost
Pipe Thickness Charts (Reference)
Carbon Steel (6″ pipe):
| Schedule | Thickness (mm) | Max Pressure (approx) |
|---|---|---|
| SCH 10 | 4.8 mm | ~10 bar |
| SCH 40 | 7.1 mm | ~20 bar |
| SCH 80 | 10.97 mm | ~35 bar |
📘 Tip: Use ASME B36.10 for carbon steel and B36.19 for stainless steel.
Final Thoughts | निष्कर्ष
Pipe thickness calculation कोई rocket science नहीं है — but it’s highly critical. A wrong thickness means:
- Leaks and accidents
- Failure under pressure
- Loss of reputation or worse — safety risk
So, whenever आप piping system design करें:
✅ Use correct formula
✅ Follow ASME codes
✅ Don’t forget corrosion and mill tolerance
✅ Select the right material
✅ Use tools like Excel, CAESAR II, or AutoPIPE for accuracy
